
CALLGOOSE

CALLGOOSE
BLOG
16 December 2024 | Tony Philip
5 Minute Read
Event-driven automation in the IT world revolves around triggering actions based on specific events or conditions. These events can be monitored and, upon detection, can trigger automated workflows, scripts, or processes to respond to the event. Here’s a list of common event-driven automation scenarios in the IT world:
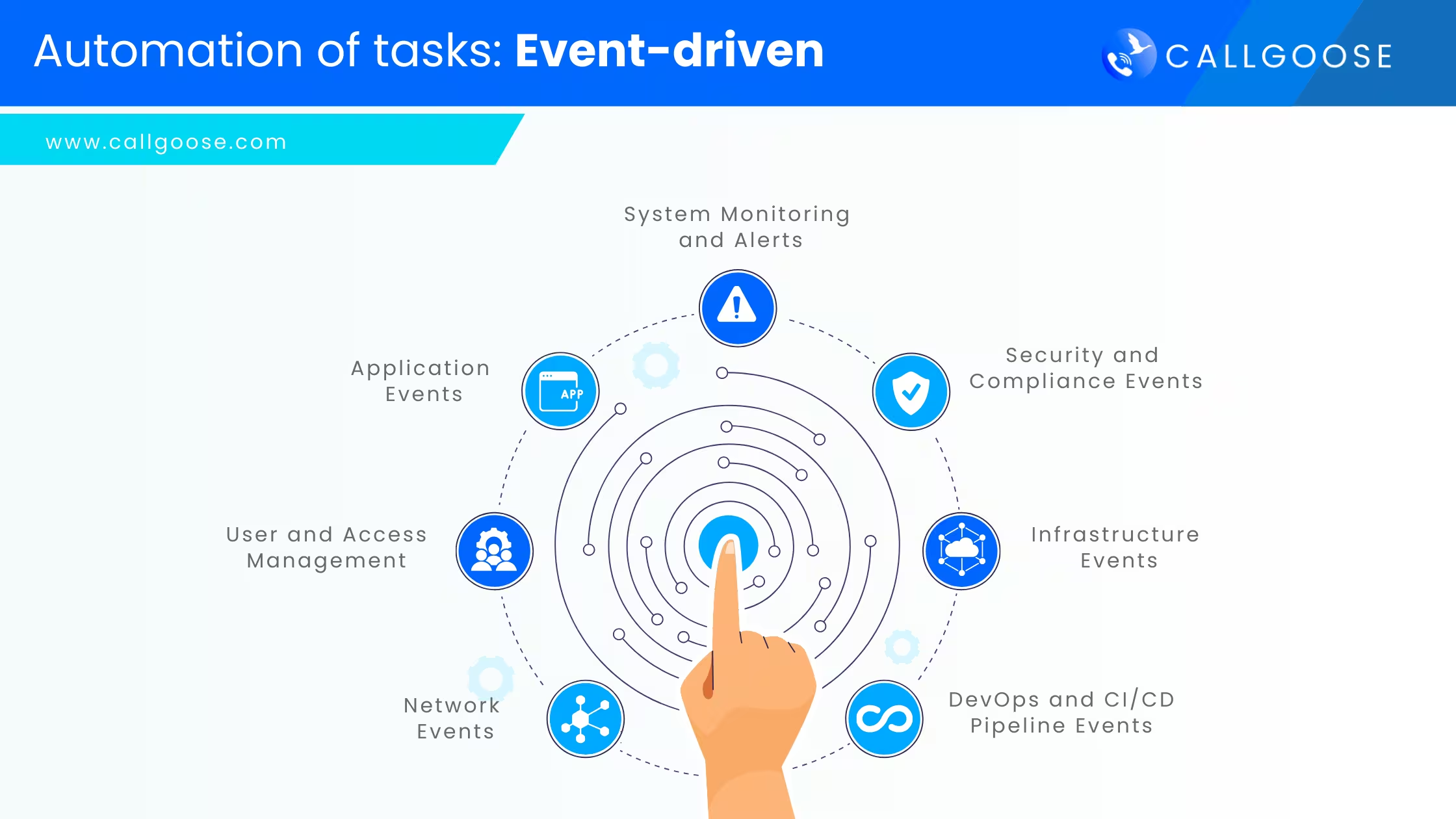
To implement event-driven automation, You can use any of your preferred tools and technologies, below are a few examples for your reference:
By leveraging these tools and using Callgoose SQIBS Incident Management and Callgoose SQIBS Automation Platform , you can set up robust event-driven automation workflows to enhance efficiency, reliability, and responsiveness in your IT operations.
Refer to Callgoose SQIBS Incident Management and Callgoose SQIBS Automation for more details
BLOG
5m Read
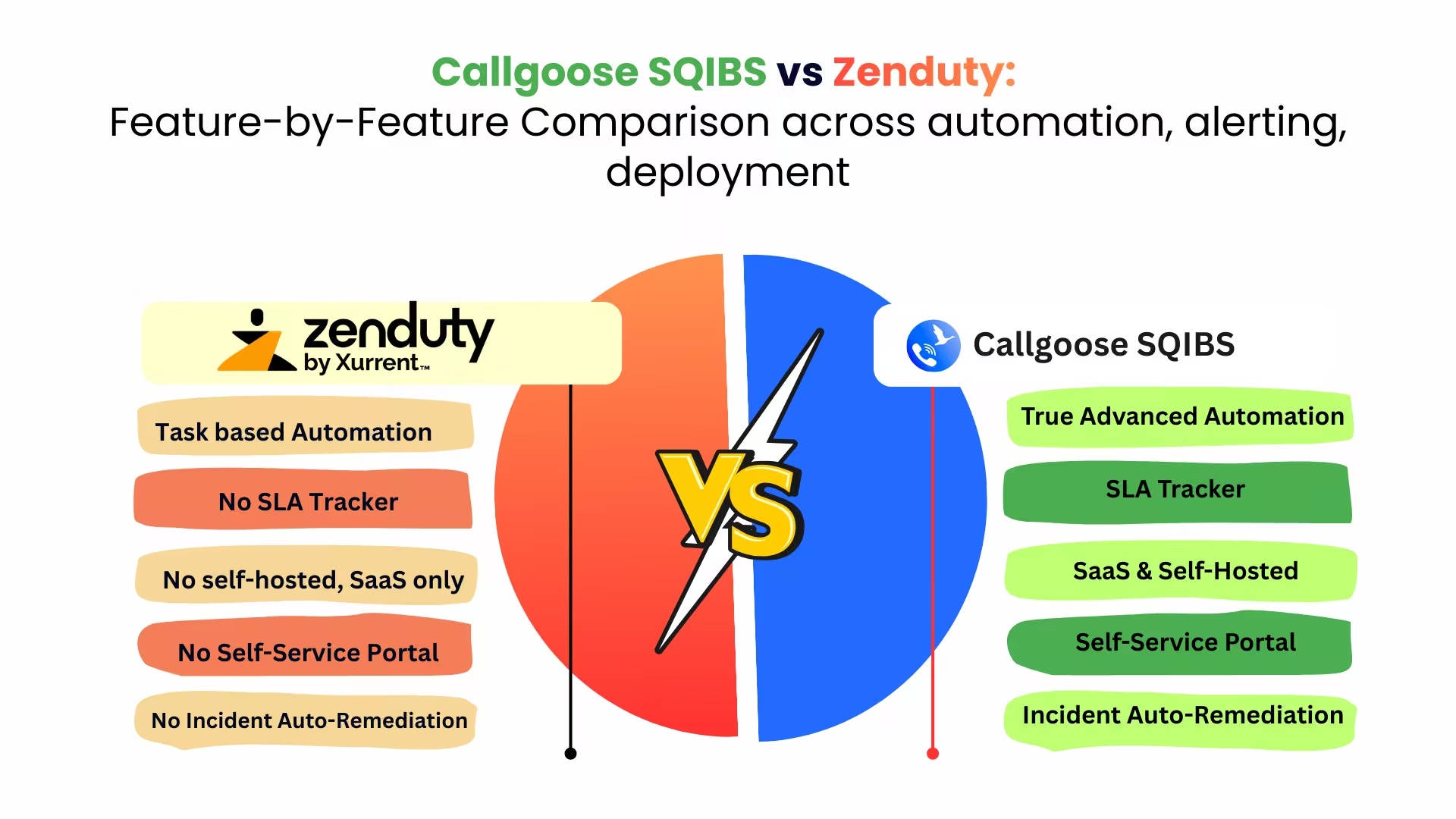
Callgoose SQIBS vs Zenduty | Detailed Feature Comparison 2026 - comparison of automation, workflows, playbooks, SLA tracking, alerting, pricing, and enterprise readiness
23 February 2026
|
Sophia Mark
Introduction As incident management platforms mature in 2026, buyers are no longer satisfied with basic alerting and task coordination. Enterprises increasingly demand automation-driven resolution, SL...

BLOG
5m Read
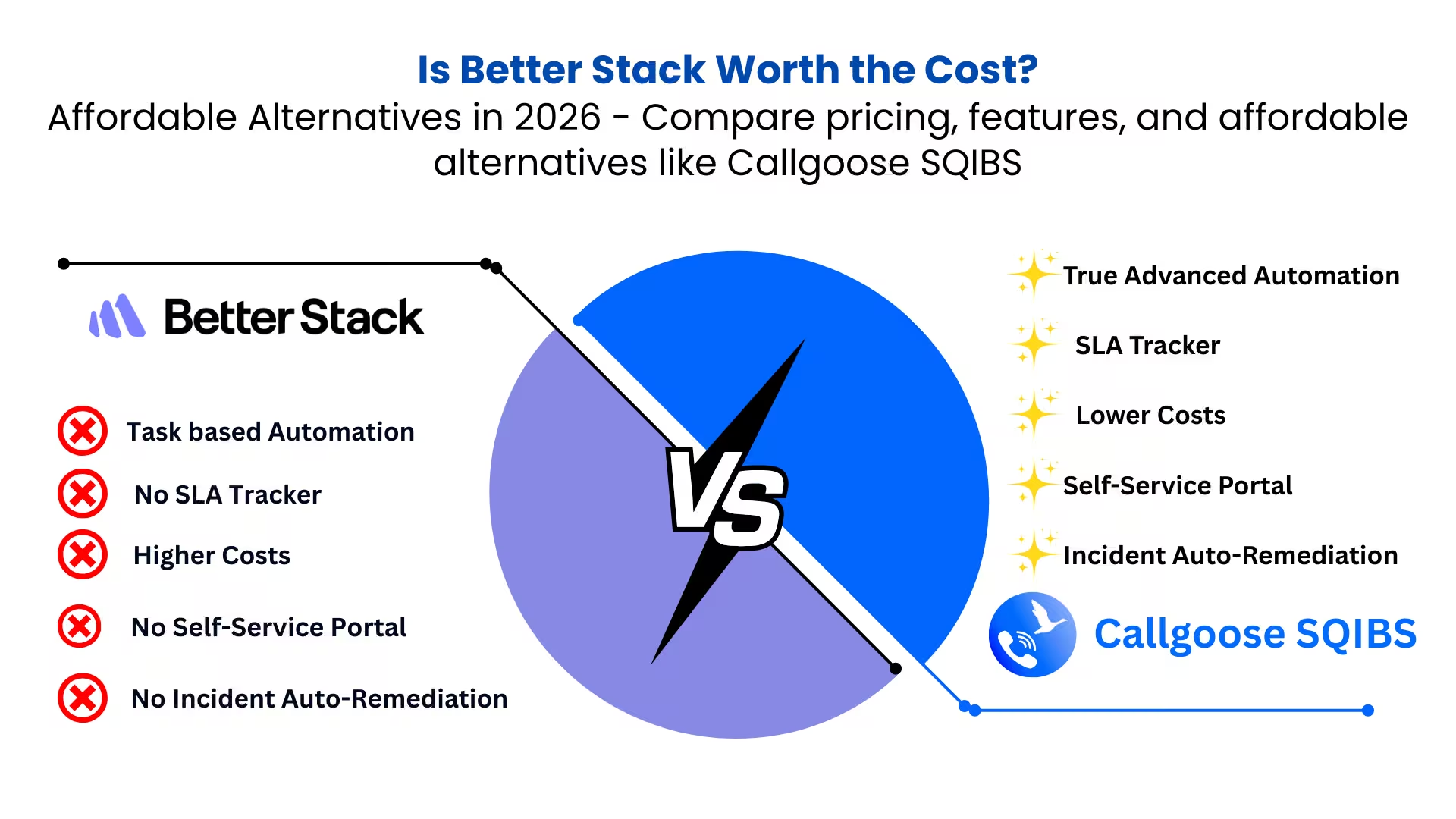
Looking for the best Better Stack alternative in 2026? Discover why Callgoose SQIBS leads in automation, SLA tracking, ChatOps, multilingual alerting, and cost efficiency
12 February 2026
|
Sophia Mark
Introduction As incident response requirements evolve in 2026, organizations are no longer satisfied with tools that only deliver notifications and coordinate manual response. Teams now require automa...
BLOG
5m Read
Explore the most affordable Better Stack alternative in 2026 - Callgoose SQIBS offers automation, SLA tracking, and ChatOps at a lower cost
12 February 2026
|
Sophia Mark
Introduction For DevOps, SRE, and IT operations teams in 2026, affordability alone is not sufficient, cost efficiency must be paired with automation depth, SLA governance, and operational scalability....
CALLGOOSE
SQIBS
Advanced Automation platform with effective On-Call schedule, real-time Incident Management and Incident Response capabilities that keep your organization more resilient, reliable, and always on
Callgoose SQIBS can Integrate with any applications or tools you use. It can be monitoring, ticketing, ITSM, log management, error tracking, ChatOps, collaboration tools or any applications
Callgoose providing the Plans with Unique features and advanced features for every business needs at the most affordable price.
Unique Features